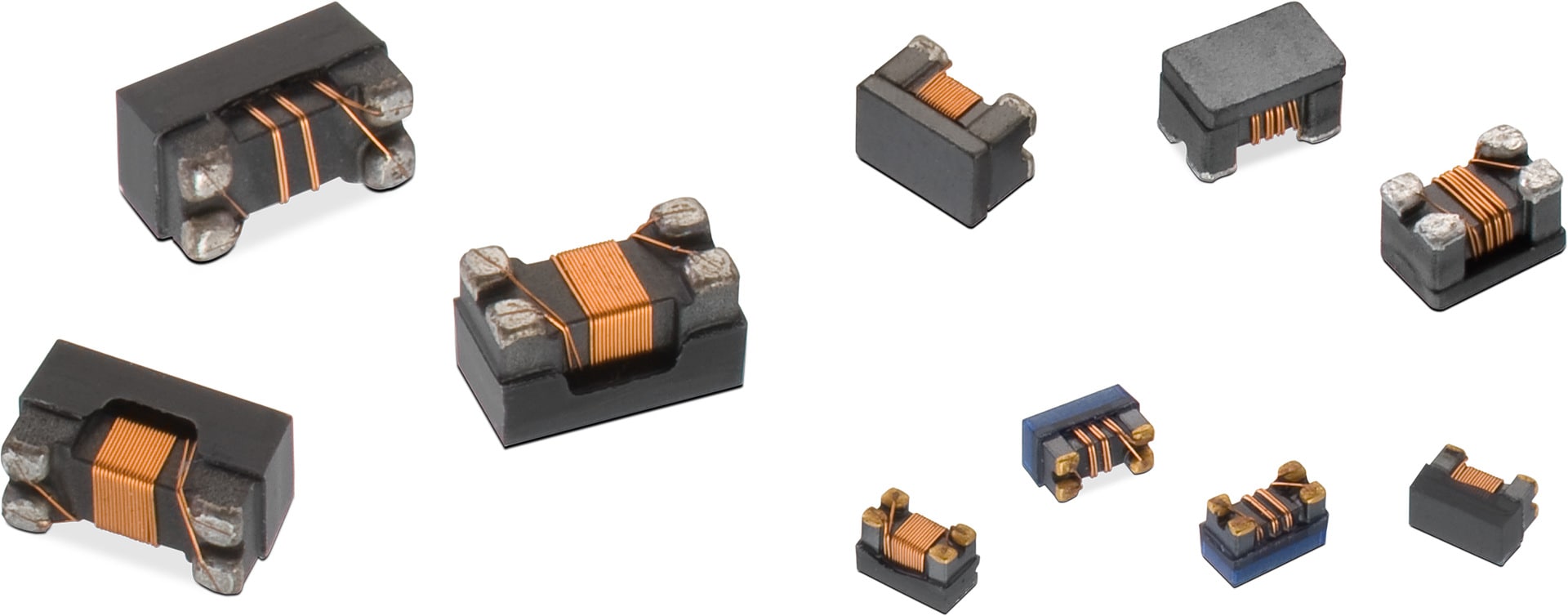
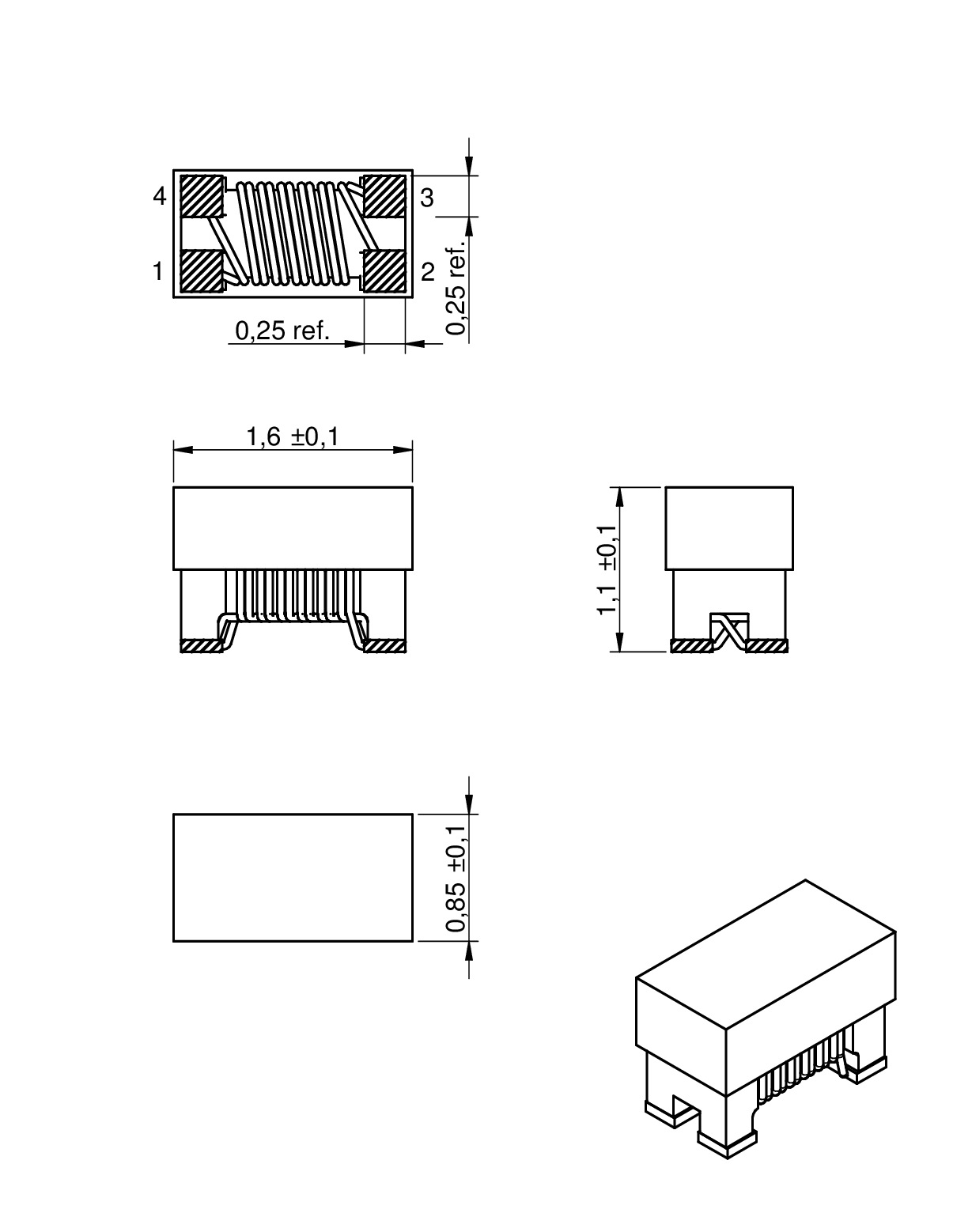
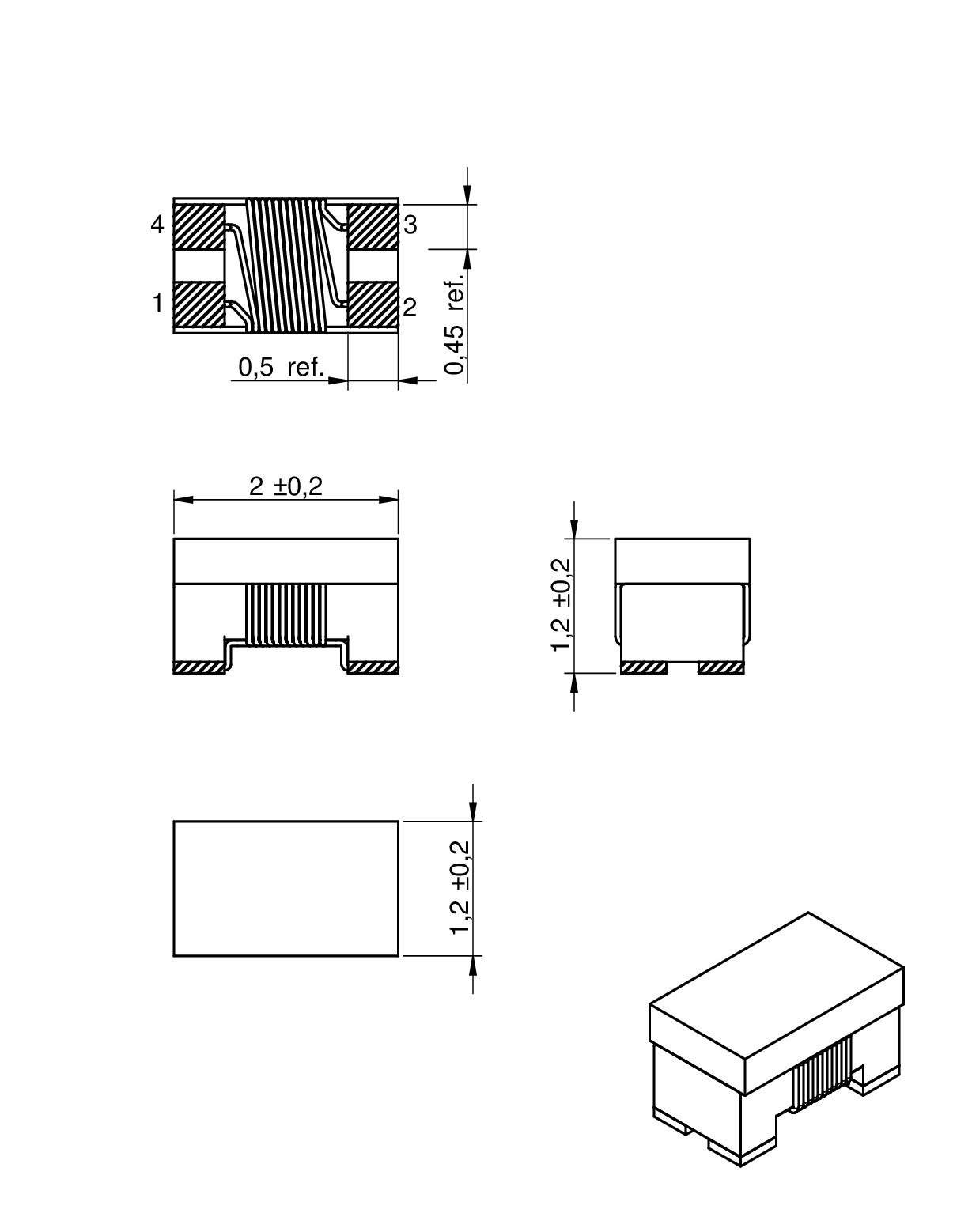
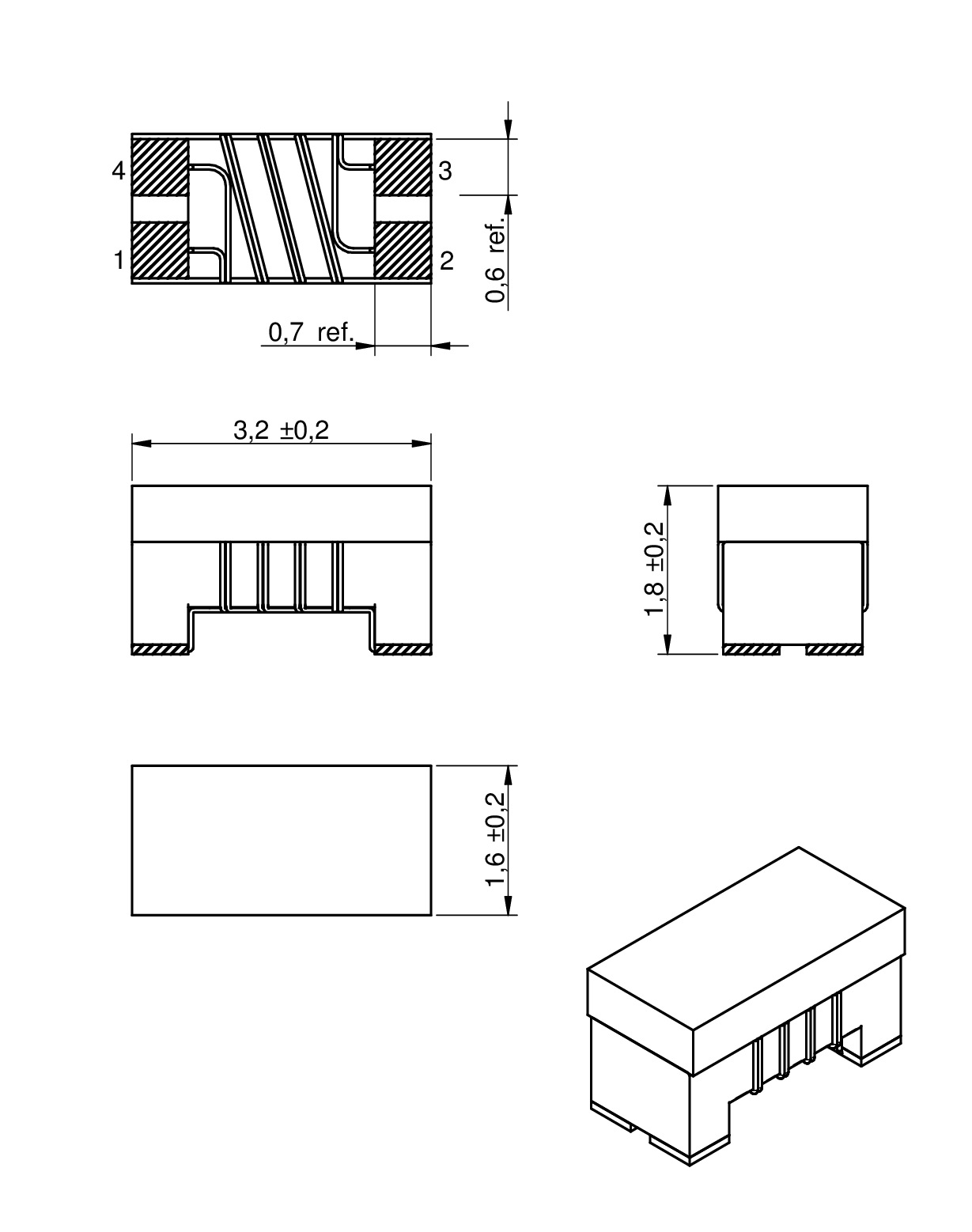
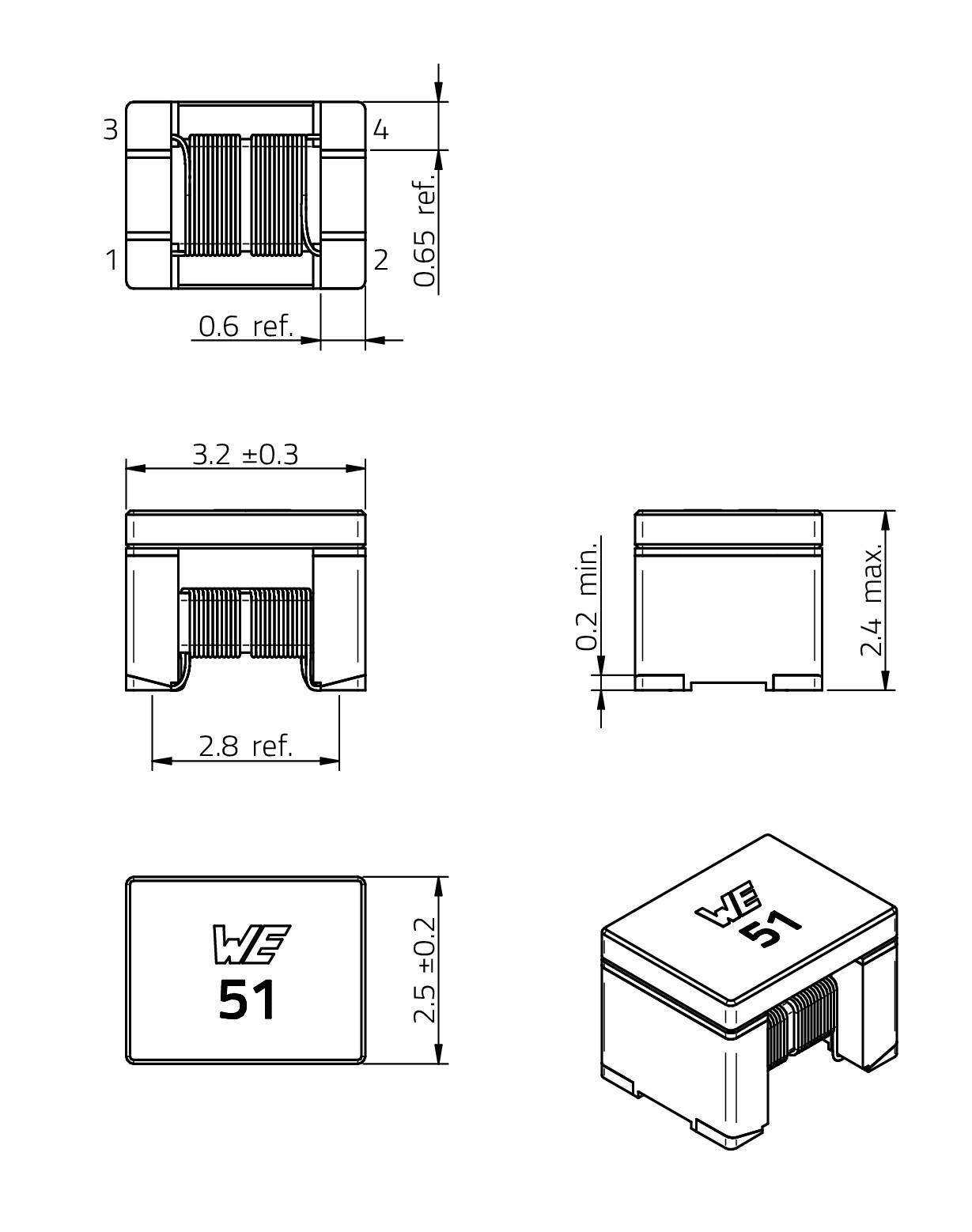
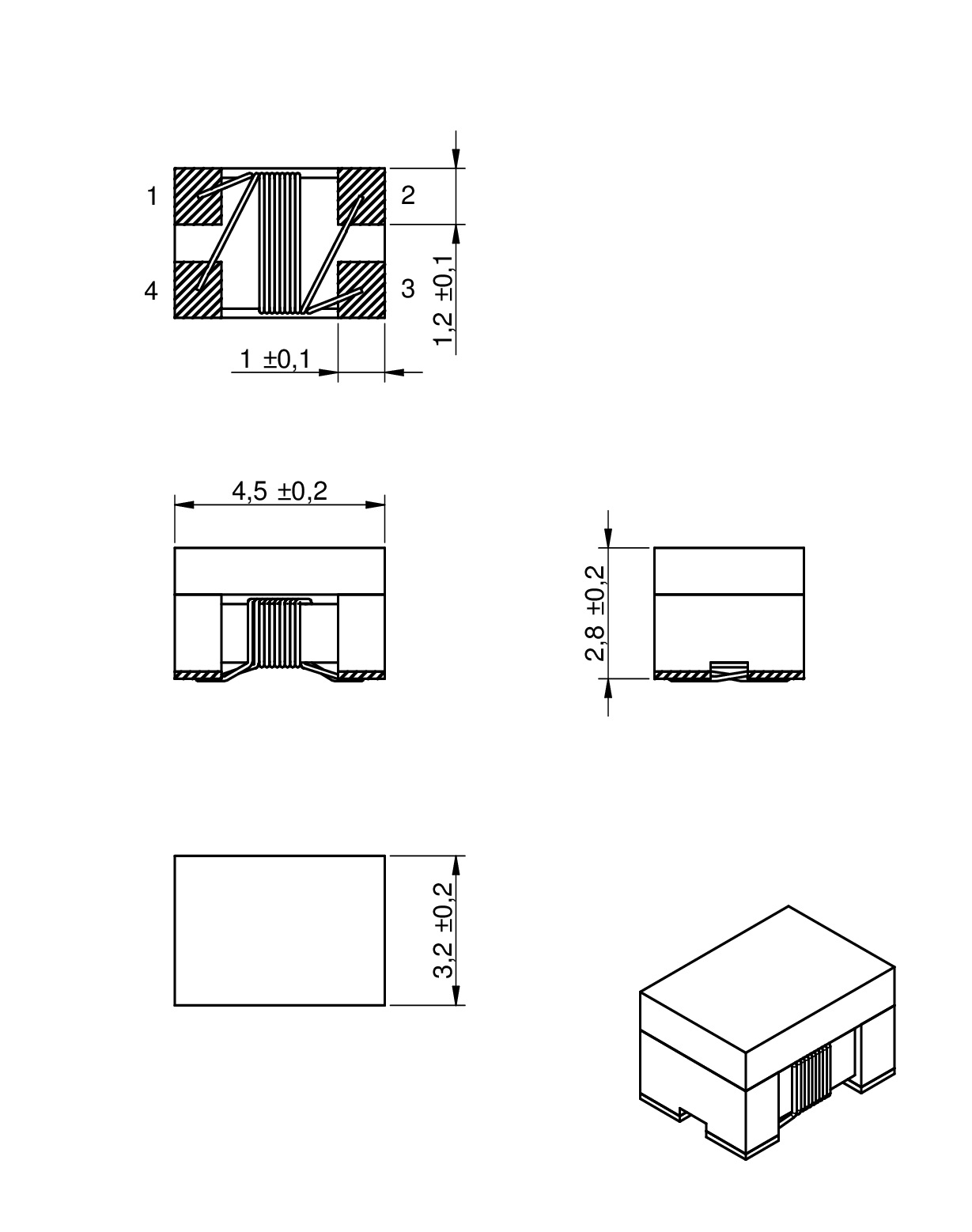
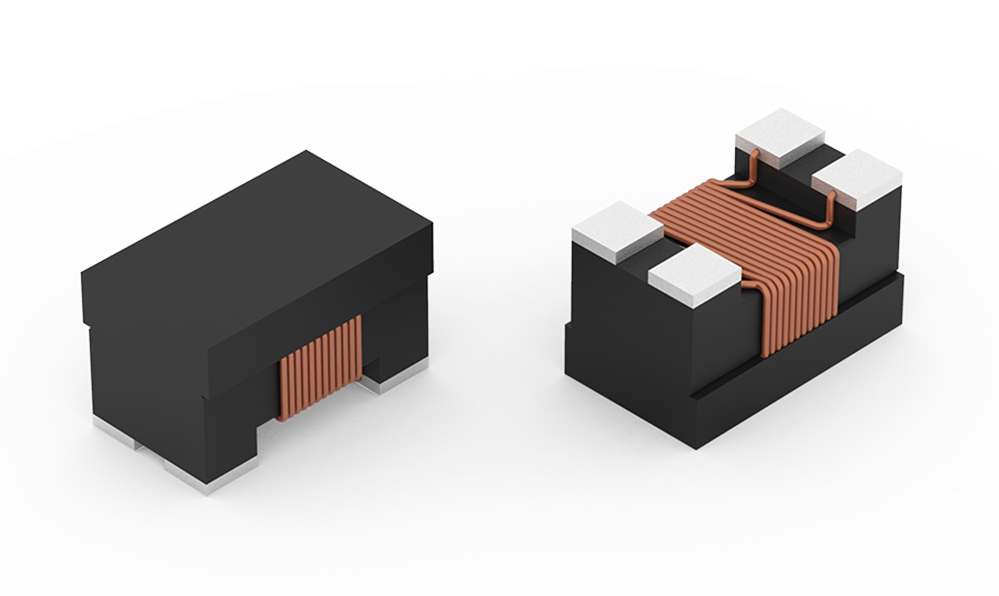
| Size | Dimensions | L (mm) | W (mm) | H (mm) | Mount | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0603 | 1.6 | 0.85 | 1.1 | SMT | |||
| 0805 | 2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | SMT | |||
| 1206 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 1.8 | SMT | |||
| NEW | 1210 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 2.4 | SMT | ||
| 1812 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 2.8 | SMT |
LTSpice files
Characteristics
- Current compensated data line filter
- High common mode noise suppression at high frequencies
- Small influence on high speed signals through winding symmetry
- Climatic category 40/105/21 (Size 0603)
- Climatic category 40/125/21 (Size 0805/1206/1812)
Reference Designs
- RD22 GB PoE+-Ethernet-USB“ adapter for industrial use with an EMC perspective
Applications
- USB 2.0
- IEEE 1394 (Firewire)
- LVDS
- High Speed Data Lines
- LAN
- Size 1812: recommended for CAN bus and CAN FD
Application Notes
- ANP002 The Protection of USB 2.0 Applications
- ANP004 Balunless measurement of mixed-mode scattering parameters
- ANP007 Effective USB 3.1 filtering and protection
- ANP024 The USB Interface from EMC Point of View
- ANP085 Single Pair Ethernet for Industrial Applications
- ANP116 Gigabit Ethernet interface from an EMC perspective
Products
| Order Code | Datasheet | Simulation | Downloads | Status | Winding Style | L (µH) | Z @ 10 MHz (Ω) | Z @ 100 MHz (Ω) | IR (mA) | RDC max. (Ω) | VR (V) | VT (V (AC)) | Application | Design Kit | Filter Stick | Filter Bag | Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 744230220 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.027 | – | 22 | 800 | 0.08 | 50 | 125 | High Speed Data Lines | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744230450 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.056 | – | 45 | 650 | 0.11 | 50 | 125 | High Speed Data Lines | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744230900 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.134 | – | 90 | 550 | 0.145 | 50 | 125 | USB 2.0 | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744230121 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.146 | – | 120 | 450 | 0.175 | 50 | 125 | IEEE 1394 / Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744230181 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.22 | – | 180 | 400 | 0.21 | 50 | 125 | IEEE 1394 / Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744230251 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.279 | – | 250 | 350 | 0.28 | 50 | 125 | High Speed Data Lines | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744231061 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.088 | – | 67 | 400 | 0.25 | 50 | 125 | High Speed Data Lines | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744231091 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.131 | – | 90 | 370 | 0.3 | 50 | 125 | USB 2.0 | 744230 | 82931060 82931100 | 82931061 82931101 | ||
| 744231121 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.166 | – | 120 | 370 | 0.3 | 50 | 125 | IEEE1394/Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744231181 | SPEC | 8 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.252 | – | 180 | 330 | 0.35 | 50 | 125 | IEEE1394/Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744231261 | SPEC | 8 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.367 | – | 260 | 300 | 0.4 | 50 | 125 | High Speed Data Lines | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744231371 | SPEC | 8 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.478 | – | 370 | 280 | 0.45 | 50 | 125 | IEEE1394/Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744232090 | SPEC | 10 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.111 | – | 90 | 370 | 0.3 | 50 | 125 | USB 2.0 | 744230 | 829999STICK | 829993BAG 829999BAG | ||
| 744232161 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.196 | – | 160 | 340 | 0.4 | 50 | 125 | IEEE1394/Firewire 400 Mbps | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744232261 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.304 | – | 260 | 310 | 0.5 | 50 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744232601 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.3621 | – | 600 | 260 | 0.8 | 50 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744232102 | SPEC | 8 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 1.263 | – | 1000 | 230 | 1 | 50 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744232222 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 2.578 | – | 2200 | 200 | 1.2 | 50 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235900 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 0.3 | – | 90 | 2000 | 0.05 | 60 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235601 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 1 | – | 600 | 1200 | 0.1 | 60 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235801 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 1.3 | – | 800 | 1000 | 0.12 | 60 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235110 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 11 | – | 5000 | 450 | 0.8 | 60 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235220 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 22 | – | 8000 | 250 | 2.65 | 60 | 125 | – | 744230 | – | – | ||
| 744235510 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 51 | 3000 | – | 200 | 1 | 60 | 125 | CAN | – | – | – | ||
| 744235101 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 100 | 5000 | – | 150 | 2 | 60 | 125 | – | – | – | – | ||
| 744232101 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 105.3 | 6000 | – | 90 | 5.5 | 50 | 125 | – | – | – | – | ||
| 744235251 | SPEC | 9 files | Active i| Production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 250 | 10000 | – | 200 | 1.6 | 60 | 125 | – | – | – | – | ||
| 744234510 | SPEC | 9 files | New i| Product is new in our portfolio and production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 51 | 2800 | – | 400 | 1.1 | 50 | 125 | CAN | – | – | – | ||
| 744234101 | SPEC | 9 files | New i| Product is new in our portfolio and production is active. Expected lifetime: >10 years. | bifilar | 100 | 5500 | – | 200 | 3 | 50 | 125 | CAN | – | – | – |
| Order Code | Datasheet | Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| 744230220 | SPEC | |
| 744230450 | SPEC | |
| 744230900 | SPEC | |
| 744230121 | SPEC | |
| 744230181 | SPEC | |
| 744230251 | SPEC | |
| 744231061 | SPEC | |
| 744231091 | SPEC | |
| 744231121 | SPEC | |
| 744231181 | SPEC | |
| 744231261 | SPEC | |
| 744231371 | SPEC | |
| 744232090 | SPEC | |
| 744232161 | SPEC | |
| 744232261 | SPEC | |
| 744232601 | SPEC | |
| 744232102 | SPEC | |
| 744232222 | SPEC | |
| 744235900 | SPEC | |
| 744235601 | SPEC | |
| 744235801 | SPEC | |
| 744235110 | SPEC | |
| 744235220 | SPEC | |
| 744235510 | SPEC | |
| 744235101 | SPEC | |
| 744232101 | SPEC | |
| 744235251 | SPEC | |
| 744234510 | SPEC | |
| 744234101 | SPEC |
| Samples |
|---|
| Order Code | Datasheet | Simulation | Downloads | Status | Winding Style | L (µH) | Z @ 10 MHz (Ω) | Z @ 100 MHz (Ω) | IR (mA) | RDC max. (Ω) | VR (V) | VT (V (AC)) | Application | Design Kit | Filter Stick | Filter Bag | Samples |
|---|
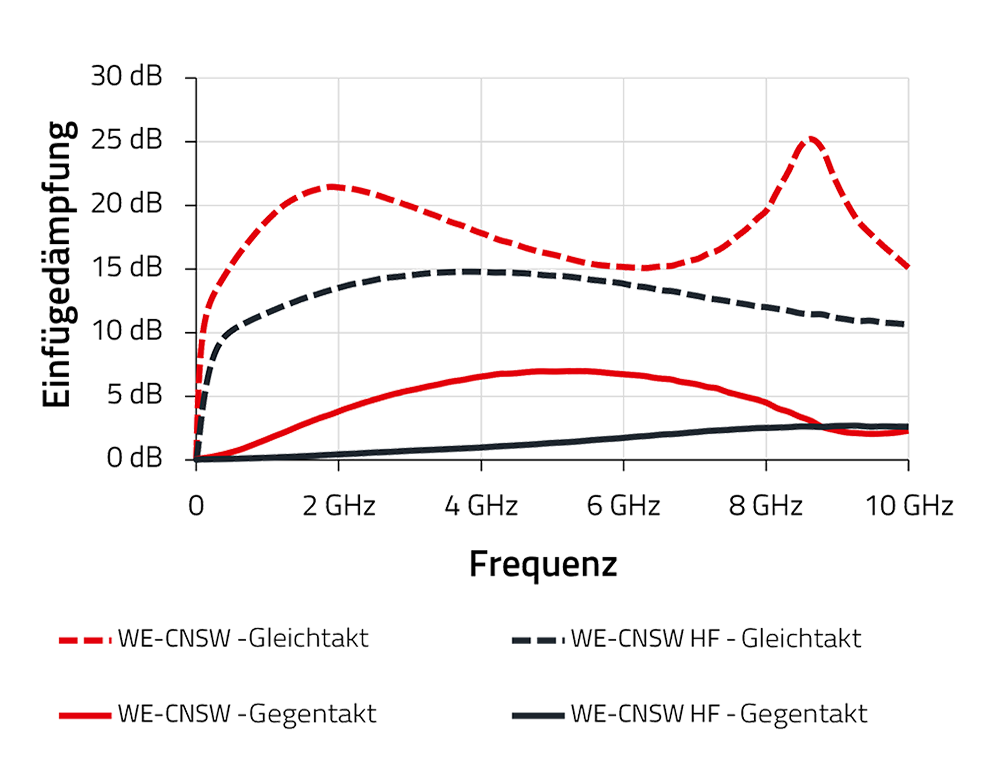
While the WE-CNSW series can work up to USB 2.0 interfaces, the WE-CNSW HF was designed to have wider frequency band to be able to work with the newest high-speed interfaces.
Common and Differential Mode Behavior
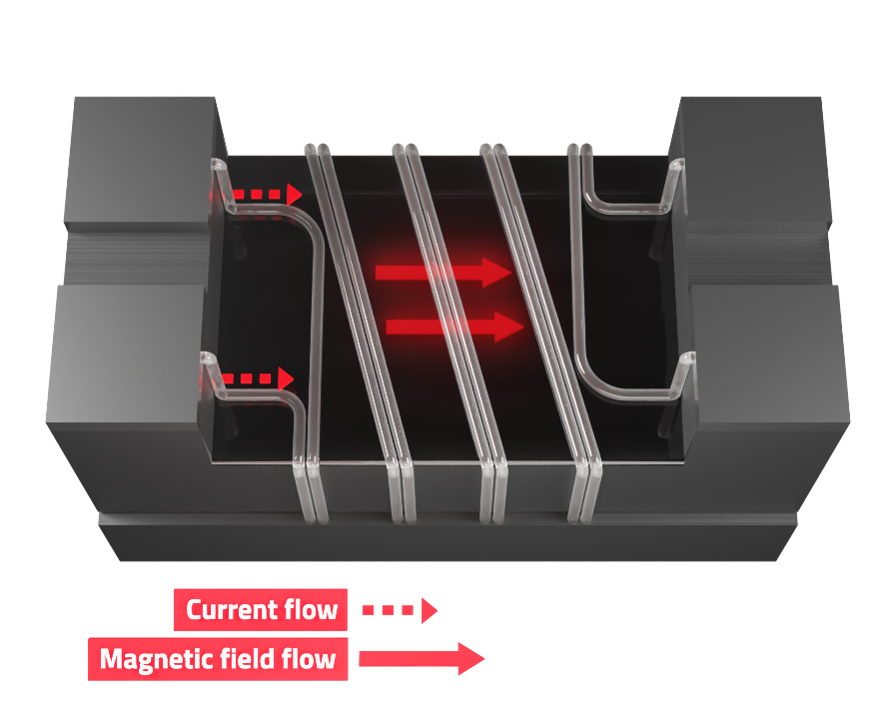
When the common mode component of a signal tries to pass through the choke, it encounters a high impedance. This is caused by the magnetization of the core and the resulting mutual inductance in the coil.
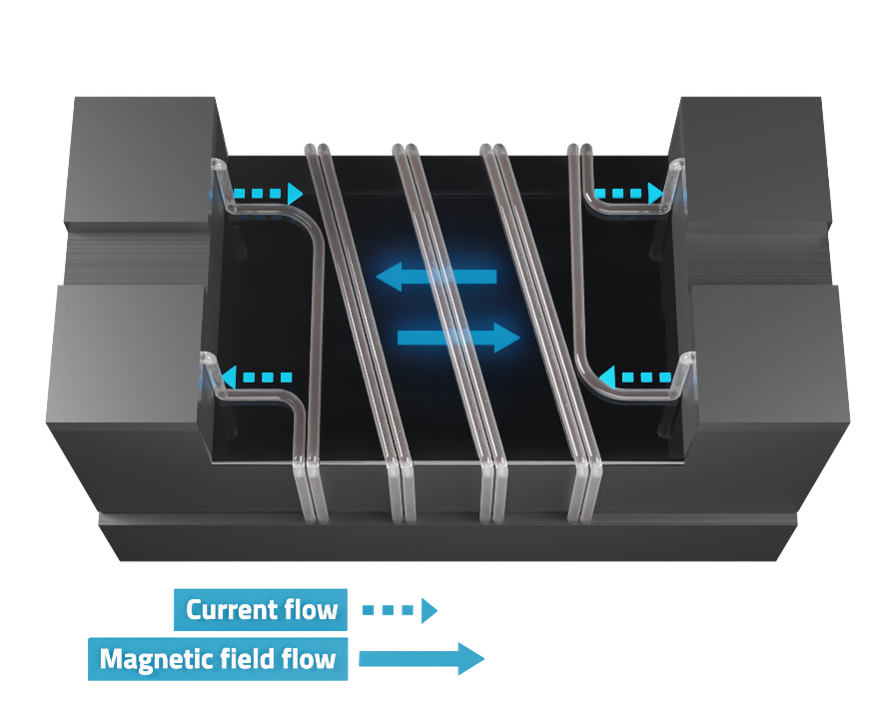
In contrast to the common mode behavior, the differential mode signal will see almost no impedance, which can be explained by the magnetic field compensation in the core. If the core is not magnetized, there is no mutual inductance so that the useful signal can pass through.
Speed up your design-in process!
The following tools and libraries make component search and selection easier for you
The online platform for easy component selection, simulation and design-in with high-precision component and circuit models.
- Common Mode Attenuation and Impedance
- Differential Mode Attenuation and Impedance
- Temperature Derating
- EDA models: Altium, Cadstar, Cadence and Eagle
- CAD files: IGS and STP
- S-Parameter, measured with 4 ports and high accuracy equipment
- Pspice
- LTspice
More Tools and Support
With the Würth Elektronik Application Guide, you can find useful information about interfaces like USB, Ethernet, LVDS and a few more.
Or use one of the various ways to get in touch with us. Feel free to contact us with your questions. Our technical specialists will be happy to help and advise you.
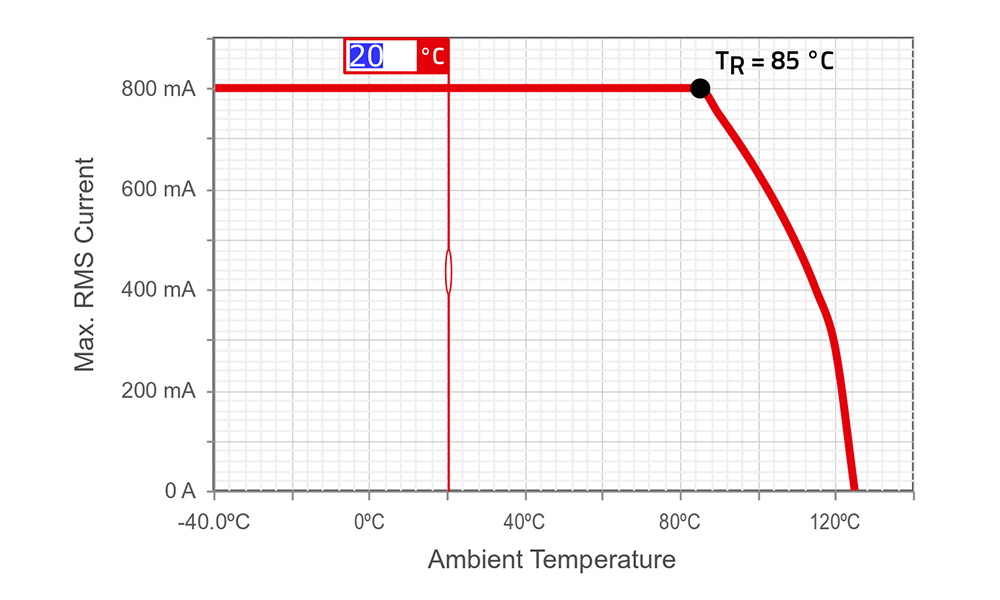
![Contens WE-CNSW temperature derating curve temperature derating curve of WE-CNSW]()
How to interpret the temperature derating curve?
Check the data sheets for operating temperature. All derating curves for our CMC can be found in REDEXPERT.
TR = Rated Temperature
Tmax = Upper limit of the operating temperature and max. temperature allowed
ΔT = Tmax – TRExample of use:
The maximum abient temperature with maximum current capability is 85 °C over this temperature the current capabilities sink. For a higher ambient temperature the maximum current can be read easily from the derating curve with the help of the chart marker.
Bifilar winding shows the lowest attenuation in differential mode. These chokes are recommended for data lines, where a high isolation is not needed and some high speed signals are involved. 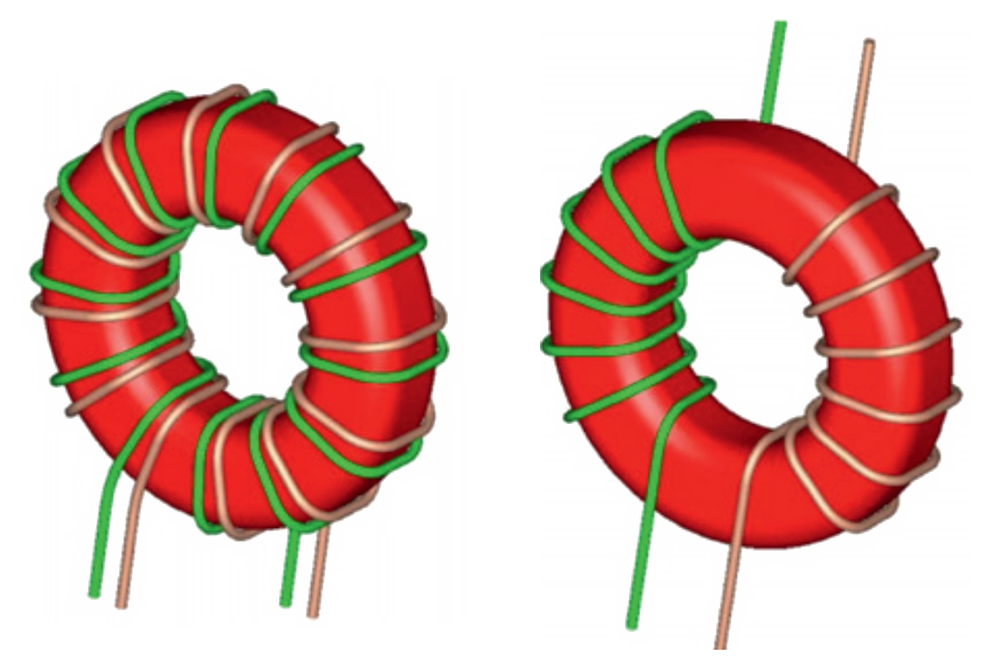
Sectional winding shows the highest attenuation in differential mode. This chokes are recommended for power lines, where a high isolation is mandatory, and the power delivery is happening at low frequency.
Assortments
Articles from this product series can be found in the following assortments:
Videos
Würth Elektronik Webinar: EMC Filters – From component to design
Videos
Würth Elektronik Webinar: Single Pair Ethernet filter design for industry
Videos
Würth Elektronik Webinar: Extremely High Speed Data Line Chokes
Videos
Würth Elektronik Webinar: Signal interface filters - effectiveness under real conditions
Videos
Würth Elektronik Webinar: Single Pair Ethernet - Filter Design and Power over Data Line
Videos
#askLorandt explains: Influence of a Common Mode Choke to the noise on the data line